I am sure everyone of us has sign-up in an online shopping website at least once. Let me consider Myntra or Paytm. When you visit the site, you come across three ways of signing up, either you can use your Facebook or Google credentials or can simply fill up a registration form for the same. When you select Google and you are only asked for your google credentials and your Myntra account is created in fraction of seconds. Isn’t that great!! But the question here is, does Myntra has access to Google’s database? OBVIOUSLY NOT!! Myntra has simply integrated Google API within their website.
Now what is this API in front of Google? When you click on Google to sign-up, Myntra takes your credentials and forwards them to Google and Google sends the user data like user Name, Image, Email Id as a response which is utilized by Myntra to create the account. In short, there is some sort of data exchange between two domains, Myntra and Google. So, the one who is responsible to process the request-response communication is known as API – Application Programming Interface. APIs are few lines of code which takes the request from the requester and gives back the response in form of data.
Are API And Web Services Similar?
An obvious question which popped-up in your mind is, So Web Service and API are same, right? My answer is, IT’S NOT. All web services are API but not all APIs are web service. Confused?? Let me explain.
As I mentioned earlier APIs are few lines of code which takes the request from the requester and gives back the response in form of data. Now suppose you are creating a utility class where you have written certain methods and can be reused in other different classes. In this case also we are exchanging data but not making use of any HTTP protocols or networks. Hence, I can term my utility class as an API but not as a Web Service.
The most popular Web Service Protocols are
SOAP – Simple Object Access Protocol
REST – Representational State Transfer
SOAP:
Recently I mentioned that web services can be called by any application irrespective of the platform being used to write the code. Now imagine a scenario where this wouldn’t have been possible. So, for every platform, there must be a web service and for every web service managing different code, HTTP or network would result in difficult maintenance.
To enable different application to use the same web service, there has to be an intermediate language – XML (Extensible Markup Language). Almost every coding platform understands XML. But the drawback is XML don’t have any fixed specification across the programming languages. Hence to avoid such scenario, SOAP protocol was introduced. SOAP is an XML-Based protocol to work over HTTP which has few fixed specifications to be used across all programming languages.
SOAP specification is known as SOAP Message.
Following are the building blocks in a SOAP Message.
SOAP Envelope: Recognizes where the XML is a SOAP. This element is mandatory.

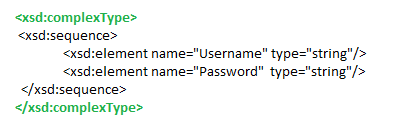
SOAP Header: Contains header information. For e.g. we need to pass username and password as a mandatory parameter in the request. We can define the same along with the datatypes under ComplexType tag. See below. This element is optional.
SOAP Body : Contains the web service URL and the elements to be passed with the request, i.e. ComplexType values.

REST-based Web Service
SOAP requires a good amount of bandwidth to exchange data. Due to the complex structure, a small group of developers came up with REST, architectural based web services, i.e. defined HTTP methods by which two applications can exchange data along with different formats like JSON, XML, Text to exchange data and response code to identify the response status. JSON is the most popular format.Following four HTTP methods are commonly used in REST-based architecture.
GET – to fetch data from the application
POST – if you want to send new data to the application for processing
DELETE – if you wish to remove an existing data
PUT – if you wish to update any existing data
Difference Between SOAP And REST
Choosing Between SOAP and REST
if your application requires high level of security
Both consumer and provider should agree to the specification format
- Use REST for,
If each operation, i.e. Create, Read, Update, and Delete are independent of each other
If you need to cache any information
The bandwidth is limited
SOAP vs REST web services
Parameter | SOAP | REST |
|---|---|---|
Acronym | SOAP stands for simple object access protocol | REST stands for REpresentational State Transfer |
Protocol vs Architectural style | SOAP is a standard protocol to create web services | Rest is architectural style to create web services. |
Contract | Client and Server are bind with WSDL contract | There is no contract between client and Server. |
Format Support | SOAP supports only XML format | REST web services supports XML, json and plain text etc. |
Maintainability | SOAP web services are hard to maintain as if we do any changes in WSDL , we need to create client stub again | REST web services are generally easy to maintain. |
Service interfaces vs URI | SOAP uses Service interfaces to expose business logic | Rest uses URI to expose business logic |
Security | SOAP has its own security : WS-security | Rest inherits its security from underlying transport layer. |
Bandwidth | SOAP requires more bandwidth and resources as it uses XML messages to exchange information | REST requires less bandwith and resources. It can use JSON also. |
Learning curve | SOAP web services are hard to learn as you need to understand WSDL , client stub | REST web services are easy to understand as you need to annotate plain java class with JAX-RS annotations to use various HTTP methods. |




No comments:
Post a Comment